The Secret Of Info About Do I Really Need 3 Phase Power

3 Phase Electricity How It Works YouTube
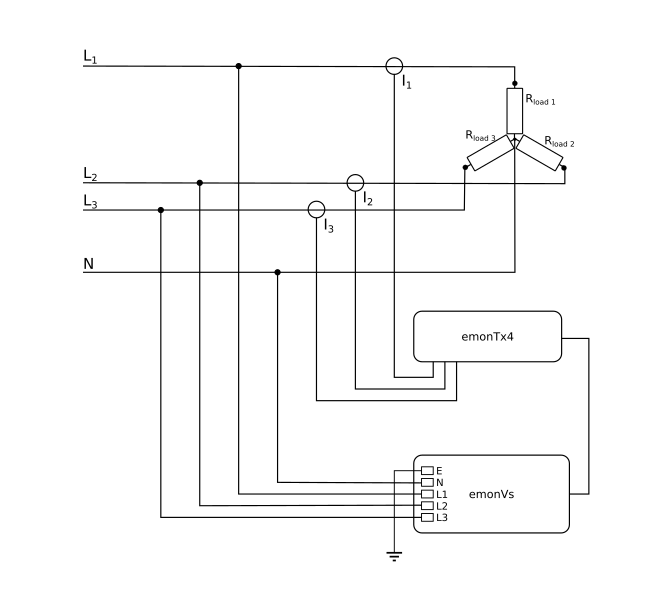
Understanding 3-Phase Power
1. What Exactly is 3-Phase Power, Anyway?
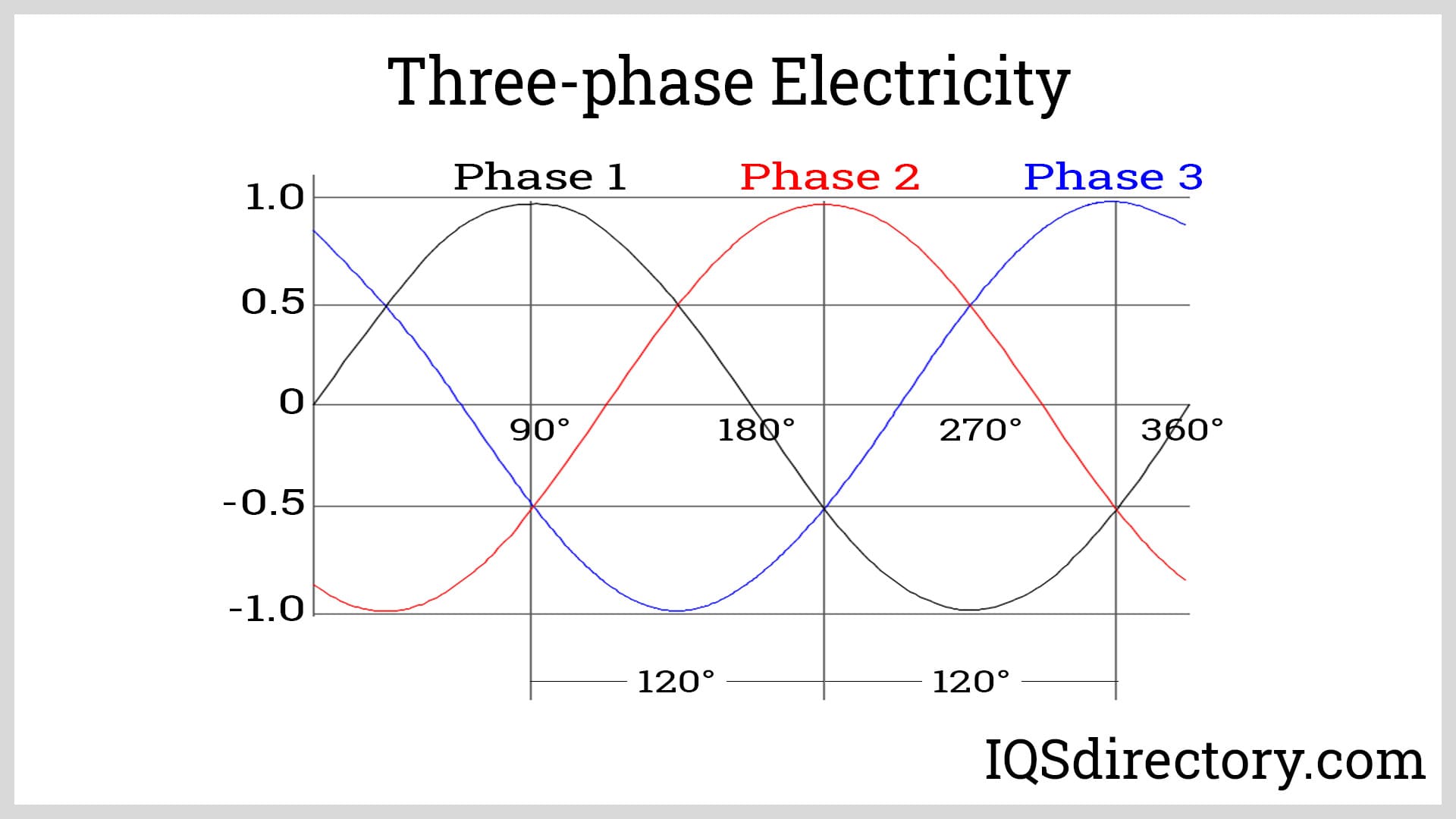
So, you're wondering about 3-phase power? Let's break it down in a way that doesn't require an electrical engineering degree. Imagine electricity as water flowing through pipes. Single-phase power is like one pipe delivering water, while 3-phase power is like three pipes all delivering water at different times, but in a coordinated way. This coordinated delivery allows for a smoother, more consistent flow of power. It's like having a team of delivery drivers instead of just one person trying to handle everything solo.
Think of it this way: single-phase power pulses on and off, delivering power in bursts. Three-phase power, however, delivers a more constant stream because the three phases are offset from each other. This difference is crucial for certain types of equipment, especially those requiring a lot of power to operate efficiently. It's why you see 3-phase power used in industrial settings and large commercial buildings where heavy machinery and large HVAC systems are the norm. Without it, things could get... well, inefficient and potentially overheated.
Now, don't get intimidated by the technical jargon. The core concept is that 3-phase power offers a more reliable and powerful electrical supply compared to its single-phase cousin. Its not just about quantity, but also about the quality and consistency of the electrical flow. This makes a significant difference when powering devices that demand a lot of energy, or precision, like certain medical devices, or CNC machines used in manufacturing.
To put it simply, single-phase is for smaller stuff, like your home appliances. Three-phase is for the big leagues, where power-hungry equipment resides. So, before you start rewiring your house, let's figure out if you really need it. And that means understanding what it actually does!

SinglePhase Vs 3Phase Power Protection What You Need To Know
Who Needs 3-Phase Power — And Who Doesn't?
2. Identifying Your Power Requirements
Alright, let's get down to brass tacks. Who really needs 3-phase power? The answer hinges on what you're trying to power. If your electrical needs consist mainly of household appliances like refrigerators, TVs, and the occasional power drill, then single-phase power is likely more than sufficient. In fact, most homes are wired for single-phase service. So, your blender is safe.
However, if you're running a commercial operation with heavy machinery, large HVAC systems, industrial-grade equipment, or specialized tools (like those used in a machine shop), then 3-phase power becomes almost essential. These types of equipment are designed to operate more efficiently and reliably with the balanced power distribution that 3-phase systems offer. Attempting to run them on single-phase can lead to performance issues, overheating, and even premature equipment failure. Think of it as trying to run a marathon on a diet of potato chips: not exactly a recipe for success.
Consider a woodworker who starts a business out of their garage. Initially, single-phase power might suffice for smaller tools. But as the business grows and requires larger, more powerful saws and planers, upgrading to 3-phase power might become a necessity to handle the increased load and prevent equipment damage. It's about scaling your power infrastructure to match the demands of your operation.
Another common scenario is when people set up specialized workshops at home for things like metalworking or automotive repair. These activities often involve tools that require a significant amount of power to operate correctly. Installing 3-phase power can provide the necessary juice to run these tools effectively, making the work safer and more efficient. It's an investment in the long-term productivity and reliability of your workspace.
The Pros and Cons
3. Benefits and Drawbacks of 3-Phase Power
Like everything in life, 3-phase power isn't a magic bullet. There are definite advantages, but also some drawbacks to consider. On the plus side, 3-phase power delivers more power using smaller wires compared to single-phase. This is because the power is distributed more efficiently across the three phases, resulting in reduced energy loss and lower operating costs over time. Think of it like using a superhighway instead of a winding country road: you get where you need to go faster and with less hassle.
Another significant advantage is the smoother, more consistent power delivery. This leads to improved performance and lifespan for many types of equipment, particularly motors and heavy machinery. The reduced vibration and stress on components translate to fewer breakdowns and lower maintenance costs in the long run. It's like choosing a well-maintained car over a rickety old clunker: you know it's going to run more reliably and require less frequent repairs.
However, there are some downsides to be aware of. The initial installation cost of 3-phase power can be significantly higher than single-phase due to the need for specialized equipment and wiring. You'll likely need to hire a qualified electrician to handle the installation process, which can add to the overall expense. It's an investment, so you need to make sure the returns are worth it.
Availability can also be a factor. Three-phase power is not always readily available in residential areas, particularly in older neighborhoods. You may need to work with your local utility company to extend 3-phase service to your property, which can involve additional costs and logistical challenges. Before making any decisions, it's wise to contact your utility provider to assess the feasibility and cost of upgrading to 3-phase power in your specific location. Be sure to ask all the difficult questions to get a complete picture.

Difference Between Single Phase And Three AC Power Supply
How to Determine Your Power Needs
4. Assessing Your Electrical Demands
So, how do you know for sure if you really need 3-phase power? The key is to accurately assess your electrical demands. Start by making a list of all the equipment and appliances that you'll be using, including their power requirements (usually measured in watts or horsepower). You can find this information on the equipment's nameplate or in the user manual. Don't just guess; accurate figures are crucial.
Next, calculate the total power consumption of your equipment. Add up the wattage or horsepower ratings of all the devices that will be running simultaneously. This will give you an estimate of your peak power demand. Remember to factor in any potential future expansion plans, as it's always better to overestimate slightly than to underestimate. No one wants to be caught short when they need extra power.
Once you have an estimate of your peak power demand, compare it to the capacity of your existing electrical service. If your current service can handle the load without overloading, then you may not need to upgrade to 3-phase power. However, if your calculations show that you're approaching or exceeding the capacity of your existing service, then it's time to consider the upgrade. Overloading your electrical system can lead to tripped breakers, power outages, and even fire hazards, so it's important to address the issue proactively.
If you're unsure about how to perform these calculations or assess your electrical system, it's always best to consult with a qualified electrician. They can conduct a thorough assessment of your power needs and provide expert guidance on whether or not 3-phase power is the right solution for your situation. They can also help you navigate the process of upgrading your electrical service, ensuring that the installation is done safely and correctly. Think of it as getting a checkup at the doctor — preventative maintenance is always a good idea.
Types, Uses And Features Of ThreePhase Transformers
The Cost Factor
5. Analyzing the Financial Implications
Let's talk money. Upgrading to 3-phase power isn't cheap, so you need to carefully consider the financial implications. The initial installation cost can vary widely depending on the complexity of the project, the availability of 3-phase service in your area, and the electrician's rates. Get multiple quotes from different electricians to ensure you're getting a fair price. Comparison shopping is key.
Don't just focus on the upfront costs, though. You also need to factor in the long-term operating costs. Three-phase power can be more energy-efficient than single-phase, which can lead to lower electricity bills over time. Additionally, the improved reliability and lifespan of equipment powered by 3-phase can result in reduced maintenance and replacement costs. So, do a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis to determine the true financial impact of the upgrade.
Also, consider any potential tax incentives or rebates that may be available for upgrading to more energy-efficient electrical systems. Many utility companies and government agencies offer programs to encourage businesses and homeowners to invest in energy-saving technologies. These incentives can help offset the initial cost of the upgrade and make it more affordable in the long run. Every little bit helps!
Finally, think about the potential impact on your business or operations. If upgrading to 3-phase power allows you to increase productivity, expand your business, or improve the quality of your products or services, then the investment may be well worth it. It's about more than just dollars and cents; it's about unlocking new opportunities and achieving your goals. So, weigh the costs against the potential benefits and make a decision that aligns with your overall objectives.
.png)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
6. Answers to Common Questions About 3-Phase Power
We understand you probably still have some questions. Here are a few common ones to help clear things up:
Q: Can I convert single-phase power to 3-phase power?A: Yes, you can! There are devices called rotary phase converters and static phase converters that can convert single-phase power into 3-phase power. However, they are not always the most efficient or reliable solution, especially for demanding applications. It's often better to upgrade to a true 3-phase service if possible.
Q: How do I know if my equipment requires 3-phase power?A: Check the equipment's nameplate. It will usually specify whether it requires single-phase or 3-phase power, along with the voltage and amperage requirements. If you're unsure, consult the equipment's user manual or contact the manufacturer.
Q: Is 3-phase power more dangerous than single-phase power?A: Both types of power can be dangerous if not handled properly. However, 3-phase power involves higher voltages and amperages, so it's even more important to work with a qualified electrician when installing or maintaining 3-phase systems. Safety first!