Looking Good Tips About What Is The Difference Between Point-to-point And Mesh Network

Unraveling the Mystery
1. Direct Connection vs. Interconnected Web
Ever wondered how your internet signal gets from point A to point B? Well, it's not always a straight shot! Two common ways networks are set up are point-to-point and mesh networks. Think of it like this: Point-to-point is like a direct phone line between two friends, while a mesh network is like a group chat where everyone's connected and can relay messages.
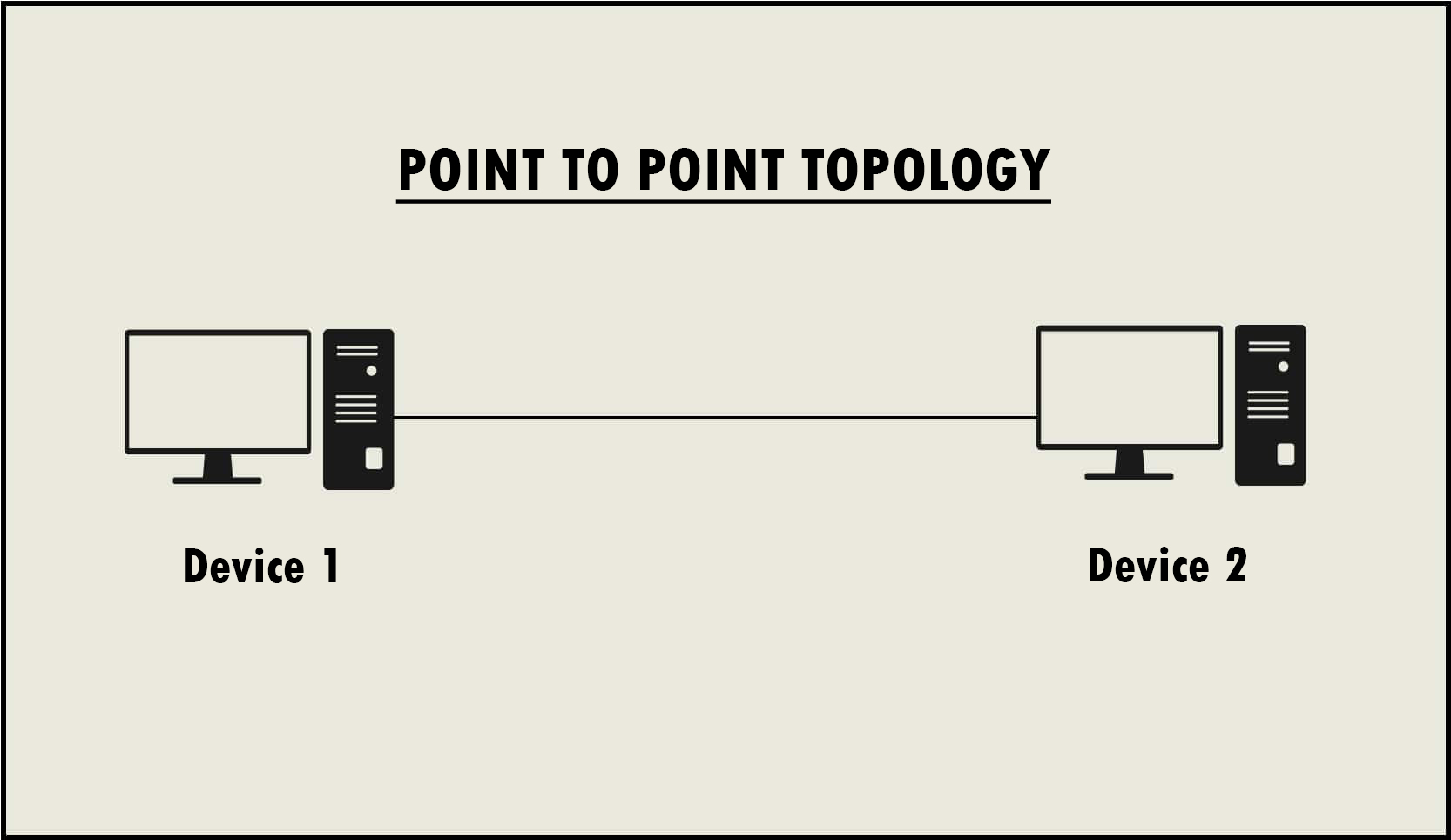
With point-to-point, you have a dedicated connection between two devices. It's simple, straightforward, and often delivers a fast, reliable connection, especially if you need low latency. Imagine setting up a secure link between two buildings for sharing files — point-to-point could be your go-to.
Now, mesh networks are a bit more complex but incredibly flexible. Instead of a single dedicated connection, devices (often called "nodes") in a mesh network connect to each other. This creates multiple pathways for data to travel. Think of it as a web or a net (hence the name!). If one path is blocked, the data can simply reroute itself through another node.
This redundancy is a huge advantage of mesh networks. They're self-healing, meaning if one node fails, the network can still function without major disruption. They're also scalable, making it easier to add more devices to your network as needed. This adaptability is especially helpful in large homes or offices where dead spots can be a real nuisance.
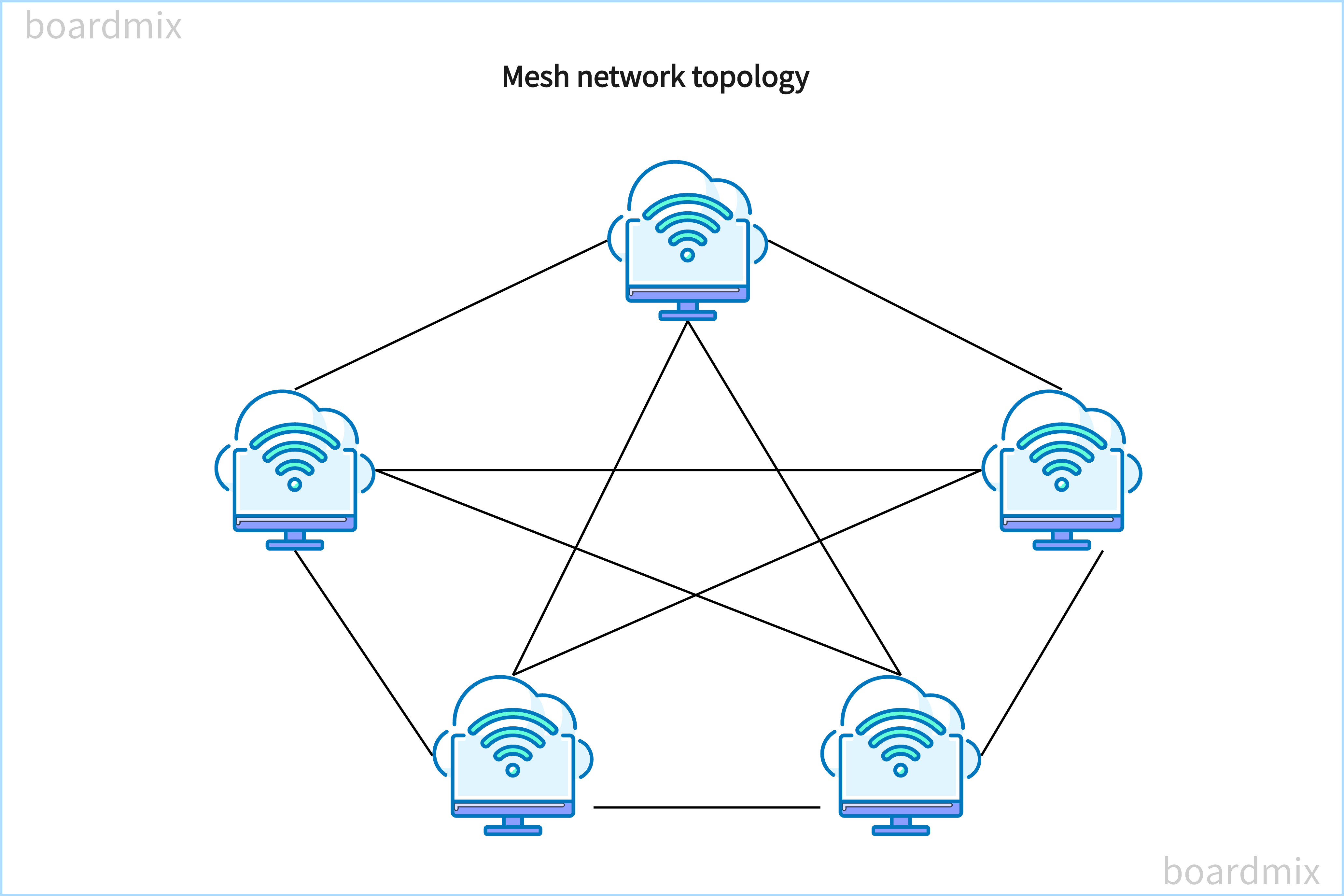
Mesh Topology Diagram Maker Mapping Network Efficiency
Breaking it Down
2. Speed, Reliability, and Scalability
Let's dive a little deeper into what sets these two network types apart. One of the key considerations is speed. Point-to-point connections often offer higher speeds and lower latency compared to mesh networks, primarily because data travels directly from one point to another without hopping through multiple nodes.
However, this simplicity comes with a potential drawback: reliability. If the single connection in a point-to-point network fails, the whole link goes down. Mesh networks, on the other hand, are far more resilient. The interconnected nature means data can be rerouted if a node fails, ensuring continuous connectivity. Its like having a backup plan... or several!
Scalability is another major difference. Adding devices to a point-to-point network can be a bit tricky, often requiring additional direct connections. With a mesh network, you can simply add more nodes, and they'll automatically connect to the existing network, expanding your coverage area. This makes mesh networks a better choice for environments where you anticipate adding more devices in the future.
Think of your smart home: Mesh networks are fantastic for handling multiple smart devices — lights, thermostats, security cameras — ensuring they all stay connected even if they're spread throughout your home. Point-to-point might be better suited for a single, high-bandwidth application that requires a dedicated connection, such as video editing or online gaming.

Point To Multipoint Network Topology
The Real-World Scenarios
3. From Rural Internet to Smart Homes
Where do these network types actually shine in the real world? Point-to-point connections are frequently used in situations where you need a high-speed, reliable connection between two specific locations. Think about rural areas where fiber optic lines aren't available. A point-to-point wireless link can bridge the gap, providing internet access to homes and businesses that would otherwise be cut off.
Another common use case is connecting buildings within a campus environment. Instead of running expensive cables between buildings, a point-to-point wireless connection can provide a cost-effective and efficient solution. Imagine a university connecting its library to the student union — point-to-point can make it happen seamlessly.
Mesh networks, on the other hand, are ideally suited for scenarios where you need widespread coverage and reliability. As mentioned earlier, smart homes are a prime example. Mesh networks eliminate dead spots and ensure all your smart devices stay connected, creating a seamless and integrated smart home experience.
They're also popular in large offices and warehouses where traditional Wi-Fi networks might struggle to provide consistent coverage. Mesh networks can create a blanket of Wi-Fi coverage, ensuring employees and devices stay connected throughout the entire space. Plus, the self-healing nature of mesh networks means less downtime and fewer headaches for IT staff.
Top 15 Point To Network Advantages And Disadvantages In 2022 EU
Choosing the Right Network
4. Budget, Coverage, and Technical Expertise
So, how do you decide which network type is right for you? Several factors come into play. First and foremost, consider your budget. Point-to-point connections can be less expensive to set up initially, especially if you only need to connect two locations. However, mesh networks might be more cost-effective in the long run if you anticipate expanding your network in the future.
Coverage area is another important consideration. If you need to cover a large area with reliable connectivity, a mesh network is likely the better choice. Point-to-point connections are more limited in terms of coverage, as they only connect two specific points. But if you only need to connect two buildings, it might be more reliable due to lower latency.
Technical expertise is also a factor. Setting up a point-to-point connection is generally simpler than configuring a mesh network. Mesh networks often require more technical knowledge to set up and manage, especially if you're dealing with a large number of nodes. Although, there are user friendly kits designed for easy setup.
Finally, think about your specific needs and priorities. Do you need the highest possible speeds and lowest latency? Or is reliability and scalability more important? Answering these questions will help you narrow down your choices and select the network type that best meets your requirements. Also, think about whether you are okay with some interference, as both point-to-point and mesh networks can suffer from interference. Just something to consider.
Point-to-Point vs. Mesh
5. The Key Takeaways
Let's quickly recap the main differences between point-to-point and mesh networks. Point-to-point offers a direct connection between two devices, providing high speeds and low latency but lacking redundancy. Mesh networks, on the other hand, create an interconnected web of devices, offering excellent reliability and scalability but potentially sacrificing some speed.
Consider your specific needs, budget, and technical expertise when making your decision. Point-to-point is ideal for connecting two specific locations with a high-speed link. Mesh networks are better suited for providing widespread coverage and reliability, especially in smart homes, offices, and warehouses.
Remember, there's no one-size-fits-all solution. The best network type for you will depend on your unique circumstances. Weigh the pros and cons of each option carefully and choose the one that best aligns with your goals and requirements. If in doubt, consult with a networking professional who can assess your needs and recommend the best solution.
Ultimately, understanding the differences between point-to-point and mesh networks empowers you to make informed decisions about your network infrastructure. Whether you're setting up a simple home network or a complex enterprise network, choosing the right network type can significantly impact your connectivity, performance, and overall user experience. So choose wisely!
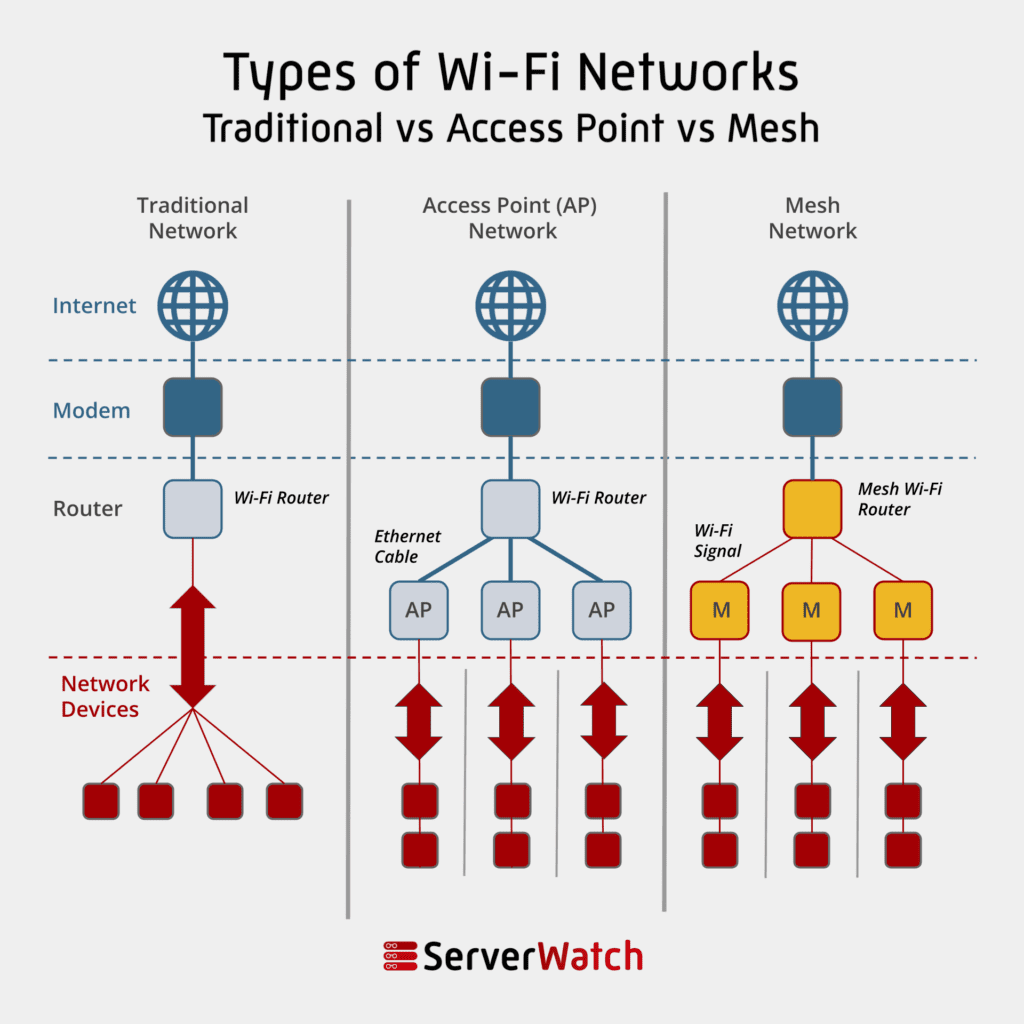
Mesh Networking Complete Guide To Understanding WiFi
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
6. Your burning questions answered!
Q: Can I combine point-to-point and mesh networks?
A: Absolutely! You can definitely use both in a hybrid setup. For example, you might use a point-to-point link to connect two buildings and then use a mesh network within each building to provide Wi-Fi coverage.
Q: Are mesh networks more secure than point-to-point?
A: Security depends more on the encryption and security protocols used than the network topology itself. Both point-to-point and mesh networks can be secured with strong passwords and encryption methods.
Q: What happens if a node fails in a mesh network?
A: That's the beauty of mesh! The network is designed to be self-healing. If a node fails, the other nodes will automatically reroute traffic through alternative paths, minimizing disruption to your network.