Outrageous Tips About Is CPU A Logic Chip
Decoding the CPU
1. Understanding the Core
Ever wondered what that square thing sitting pretty (or not so pretty, depending on your cable management skills) inside your computer is? That's the CPU, or Central Processing Unit. Think of it as the brain of your machine, constantly crunching numbers and making decisions faster than you can say "supercalifragilisticexpialidocious" (try saying that three times fast!). But is it just a logic chip? Well, that's where things get interesting. It's a bit like saying a gourmet burger is just a patty — technically correct, but missing the whole delicious story.
At its heart, the CPU is a complex collection of logic gates. These gates, built from transistors (tiny switches, billions of them!), perform basic logical operations like AND, OR, and NOT. It's all binary; 1s and 0s zipping around at lightning speed. These simple operations are the building blocks of everything your computer does, from displaying cat videos to running complex simulations. So, in that sense, yes, it's a logic chip. But it's a very sophisticated one, like comparing a simple calculator to a supercomputer.
The key is complexity and integration. A modern CPU doesn't just have these logic gates scattered randomly. They're organized into incredibly complex circuits and structures designed for specific tasks. These include arithmetic logic units (ALUs) for performing calculations, control units for managing the flow of instructions, and registers for storing data temporarily. All of these are intricately woven together to execute the instructions that make your computer tick.
Think of it like a symphony orchestra. Each musician plays a single instrument, producing individual notes. But when they all play together under the conductor's direction, they create a beautiful and complex piece of music. Similarly, each logic gate performs a simple operation, but when they all work together under the CPU's architecture, they create the incredible processing power we rely on every day.
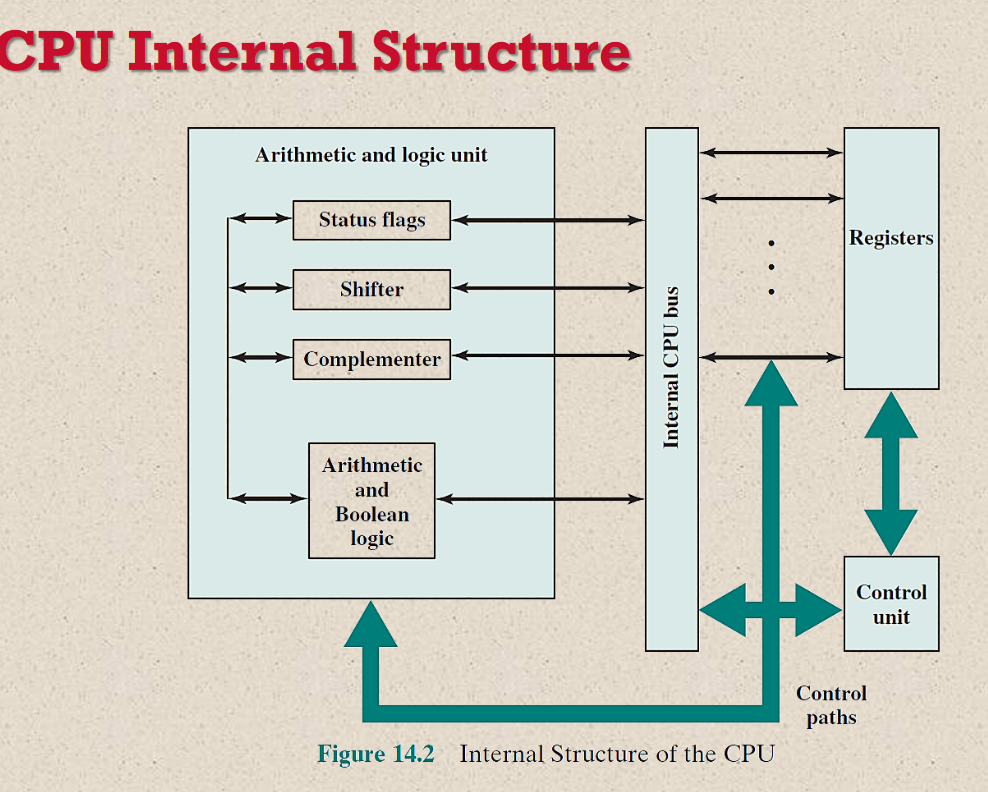
Internal Structure Of Cpu With Diagram Circuit A
Delving Deeper
2. More Than Meets the Eye
So, we've established that the CPU is built on logic gates, but there's so much more happening inside that silicon wafer. Modern CPUs incorporate advanced technologies to boost performance and efficiency. We're talking about things like pipelining, where multiple instructions are processed simultaneously, and branch prediction, where the CPU tries to guess what instruction will be needed next to avoid delays. Its like predicting the future, but with code!
Then there's caching. CPUs have multiple levels of cache memory, small, fast storage areas that hold frequently accessed data. This reduces the need to constantly fetch data from slower main memory, significantly speeding up processing. Imagine having a cheat sheet for all your frequently used formulas right next to you during an exam — that's essentially what cache memory does for the CPU. It's all about efficiency and speed.
And let's not forget about multicore CPUs. These have multiple processing cores on a single chip, allowing them to perform multiple tasks simultaneously. It's like having multiple brains working together, each handling a different part of the workload. This is particularly useful for multitasking and running demanding applications. Your ability to watch a video, browse the web, and download a file all at the same time? Thank multicore CPUs.
Furthermore, the architecture of the CPU itself plays a crucial role. Different CPUs have different designs, with varying numbers of cores, cache sizes, and clock speeds. These differences affect performance, power consumption, and cost. Choosing the right CPU for your needs can make a huge difference in your computing experience. It's like picking the right tool for the job — a hammer won't do you much good if you're trying to screw in a screw.

Computer Chips Design
Architecture Matters
3. Different Flavors of Processing Power
The architecture of a CPU — how it's all laid out and connected — is incredibly important to its overall performance and what it's good at. Think of it as the blueprints for a skyscraper; a bad design leads to wobbly walls and leaky roofs, but a good one lets you build something amazing. We've got two major players in the CPU game: Intel and AMD. While both make CPUs out of, essentially, logic gates, they approach the design and implementation in different ways.
Intel CPUs are often known for their strong single-core performance. This means they can handle individual tasks very quickly. This can be particularly useful for applications that rely heavily on a single thread of execution. They often prioritize maximizing clock speeds and optimizing the instruction pipeline for speed. It's all about getting the job done fast, even if it means focusing on one thing at a time.
AMD CPUs, on the other hand, have been gaining ground in recent years with their focus on multicore performance and value. They pack more cores into their CPUs at competitive price points, making them a great choice for multitasking and demanding workloads. This gives them an edge in applications that can take advantage of multiple threads, such as video editing and gaming. Its a 'strength in numbers' approach.
Beyond just Intel and AMD, ARM-based CPUs are also making a big splash, especially in mobile devices and increasingly in laptops. These CPUs are known for their power efficiency, squeezing as much performance as possible out of every last drop of battery life. They achieve this through a different architecture that emphasizes simplicity and low power consumption. They are the marathon runners of the CPU world; prioritizing endurance over raw speed.

Beyond Desktop
4. The Reach of Processing Power
CPUs aren't just confined to desktop computers and laptops. They're everywhere! From your smartphone to your smart refrigerator (yes, even your fridge might have a CPU!), these tiny powerhouses are constantly working behind the scenes. The CPUs in these devices might not be as powerful as the ones in your gaming rig, but they're still essential for their functionality. They are the unsung heroes of the digital world.
Embedded systems, which are specialized computer systems designed for specific tasks, also rely heavily on CPUs. These systems can be found in everything from cars to medical devices to industrial equipment. They often use specialized CPUs that are optimized for low power consumption and real-time performance. This is where things get really cool, from controlling the anti-lock brakes in your car to monitoring a patient's heart rate, CPUs are making a difference.
Even in the cloud, CPUs are the workhorses that power the internet. Data centers are filled with servers, each containing multiple CPUs, that handle everything from storing your cat pictures to running complex AI algorithms. The cloud wouldn't exist without the processing power provided by these CPUs. They are the backbone of the internet, quietly and efficiently handling the world's data.
And of course, the gaming consoles we love wouldn't exist either. The CPUs inside consoles like the PlayStation and Xbox are specifically designed to deliver high-performance gaming experiences. They're constantly pushing the boundaries of what's possible in terms of graphics and gameplay. They are the wizards behind our immersive digital adventures.
![CPU Cores Vs Logical Processors & Threads [Explained 2024] CPU Cores Vs Logical Processors & Threads [Explained 2024]](https://10scopes.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/processor-with-and-without-threads.jpg)
CPU Cores Vs Logical Processors & Threads [Explained 2024]
Wrapping Up
5. It's Complicated, But Worth Understanding
So, is a CPU a logic chip? Yes, but it's so much more than that. It's a highly complex and integrated system that combines logic gates, advanced architectures, and various technologies to deliver the processing power we rely on every day. It's the brain of our computers, the engine of the internet, and the heart of countless devices that make our lives easier and more entertaining. It's the culmination of decades of engineering ingenuity. A true marvel of modern technology!
Understanding the basics of CPU architecture and functionality can help you make informed decisions when choosing a computer or other device. It can also give you a greater appreciation for the technology that powers our modern world. Knowing how a CPU works is a bit like knowing how an engine works in your car — it allows you to understand its capabilities and limitations.
The evolution of CPUs continues, with new technologies and architectures constantly being developed. From quantum computing to neuromorphic chips, the future of processing power is full of exciting possibilities. Who knows what amazing things we'll be able to do with computers in the years to come? This is truly the dawn of a new age in computing.
So the next time you're using your computer, take a moment to appreciate the little logic chip that's making it all happen. It may seem like a small and insignificant component, but it's actually one of the most important and powerful technologies ever created. It's like the little engine that could — constantly pushing the boundaries of what's possible.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
6. Your Burning CPU Questions Answered
Q: What's the difference between a CPU and a GPU?
A: While both are processors, they have different strengths. CPUs are general-purpose, good at a wide variety of tasks. GPUs (Graphics Processing Units) are specialized for handling graphics and parallel processing, making them ideal for gaming and video editing. Think of it like this: the CPU is the all-rounder athlete, while the GPU is the specialized sprinter.
Q: What does "clock speed" mean?
A: Clock speed, measured in GHz (gigahertz), indicates how many instructions a CPU can process per second. Higher clock speeds generally mean faster performance, but it's not the only factor. Architecture, core count, and cache size also play significant roles. It's like saying a car's speed depends only on how fast the engine revs — you'd also need to consider the aerodynamics and the tires!
Q: Is it safe to overclock my CPU?
A: Overclocking pushes your CPU beyond its rated speed, potentially increasing performance. However, it also generates more heat and can damage your CPU if not done carefully. It's like pushing your car's engine to its limits — you might get a little more speed, but you risk blowing a gasket. Proceed with caution and proper cooling!
Q: How long does a CPU typically last?
A: With proper care (good cooling, stable power supply), a CPU can last for many years, often outlasting other components in your computer. It's not uncommon for a CPU to still be working strong after 5-10 years. They are the workhorses of the computer world; built to last.